Introduction
In this second part of the series, we will be setting up a Jenkins Shared library to execute our Jenkins jobs. As the complexity and number of jobs you maintain grow, the use of Shared Libraries provides the ability to share and reuse code across jobs for CI and CD processes.
In order to set up a practical application with our seedJob, we will modify seed.groovy to build a Pipeline job (deployment job) and a Multibranch Pipeline job (test job). By the end of this series, you will have a foundation set up to onboard micro services consistently as well as execute certain stages specific to the Jenkins jobs you are running.
Source Code
The source code is available below
- Jenkins Shared Library (
microservice-pipelines) poc-microJHipster microservice
Prerequisites
- Jenkins running in a Docker container built from
kcrane121/maven-jenkins:blog. seedJobset up from Part 1.
Part 2 Goals
- Configure Jenkins to use
microservice-pipelines
as our Shared Library for executing jobs.- As the number of jobs you use in Jenkins grows, the amount of duplicate code between jobs can become overwhelming to maintain while new requirements for all of your jobs are introduced. The Shared Library functionality within Jenkins allows you to consolidate the code you use within one repository to be shared across your jobs.
- Configure
seed.groovyto create a Pipeline Job (deployment job) and Multibranch Pipeline Job (test job) per service. - Create
jenkinsJob.groovyto be used by our micro services as the entry point into our Shared Library. - Set up a
Jenkinsfileinpoc-microto usemicroservice-pipelinesShared Library.
Goal 1
Configure default Shared Library set up for Jenkins
Since we will be using a Shared library, Jenkins needs to be set up to use our Shared Library.
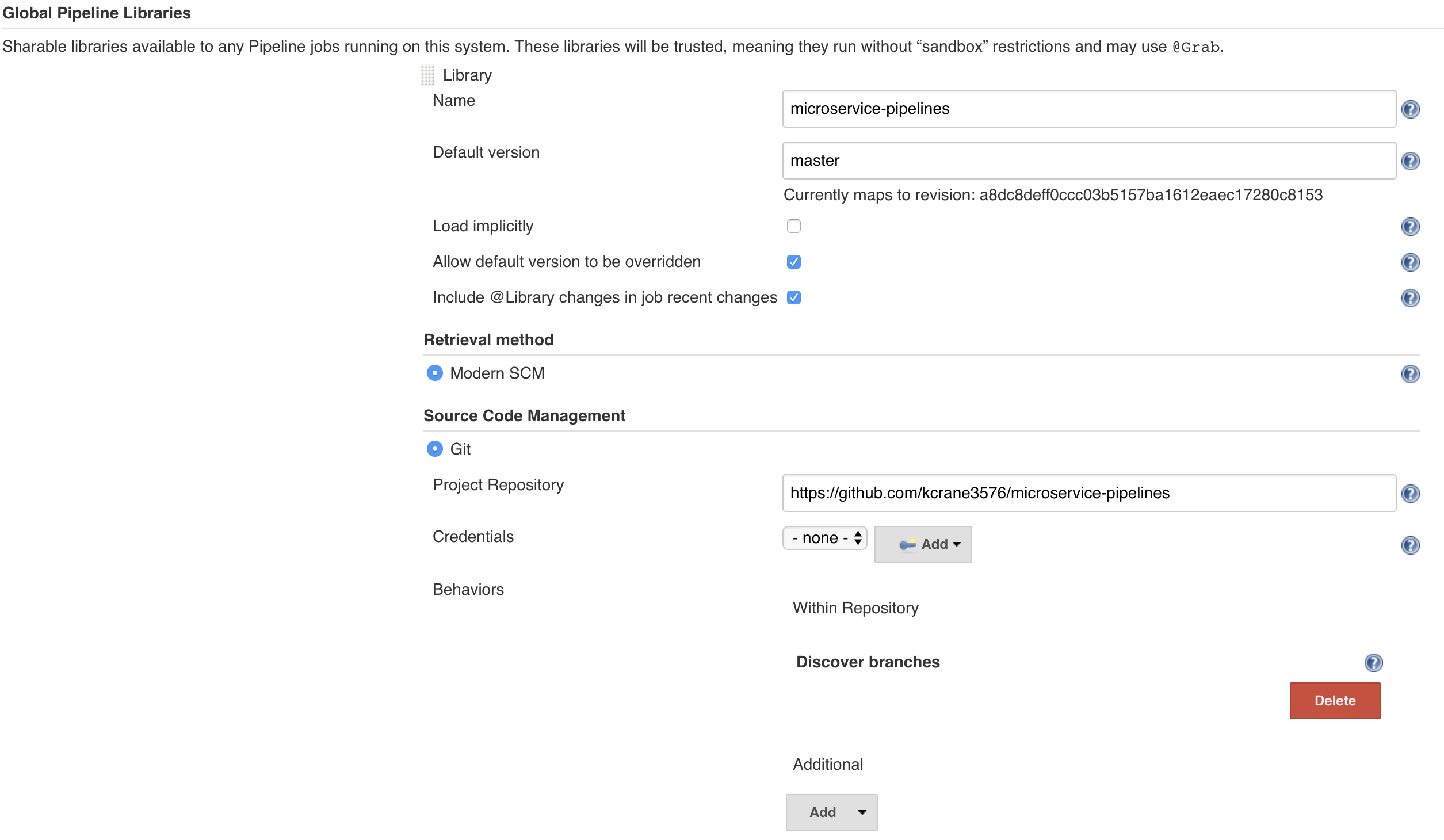
- Navigate to
Dashboard> selectManage Jenkins> selectConfigure System> scroll down toGlobal Pipeline Libraries> selectAdd - Enter
microservice-pipelinesin theNamefield - Enter
masterinDefault Version- This tells jenkins which branch of our Shared Library we plan to use by default.
- Under
Source Code Management, selectGit - In the
Project Repositoryfield, enterhttps://github.com/kcrane3576/microservice-pipelines> selectSave.
Goal 2
We are going to modify seed.groovy to build a Pipeline job and Multibranch Pipeline job for all services we onboard.
Update seedJob to use a part2 branch we will create in microservice-pipelines
- Navigate to
Dashboard> selectseedJob> selectConfigure. - Under
Source Code Management, change theBranch Specifierto*/part2.
Updating microservice-pipelines to build our deployment and test jobs
We are going to leave the master branch of microservice-pipelines alone to ensure it works with Part 1 of this series. In order for us to do this, we will introduce the changes to the seed.groovy job on branch part2 of microservice-pipelines.
Adding pipelineJob and multibranchPipelineJob to seed.groovy
- Create a new branch
part2inmicroservice-pipelines. - In the
part2branch, remove the original code inseed.groovyand paste in the below code.- For a better understanding of the
pipelineJobandmultibranchPipelineJob, make sure to go back and check the Jenkins Job DSL API.
- For a better understanding of the
def createDeploymentJob(jobName, repoUrl) {
pipelineJob(jobName) {
definition {
cpsScm {
scm {
git {
remote {
url(repoUrl)
}
branches('master')
extensions {
cleanBeforeCheckout()
}
}
}
scriptPath("Jenkinsfile")
}
}
}
}
def createTestJob(jobName, repoUrl) {
multibranchPipelineJob(jobName) {
branchSources {
git {
remote(repoUrl)
includes('*')
}
}
triggers {
cron("H/5 * * * *")
}
}
}
Add method to execute the building of the pipelineJob and multibranchPipelineJob
Finally we will need to trigger the building of the specific poc-micro_deploy and poc-micro_test jobs we are onboarding.
- Hard code the
repovariable withhttps://github.com/kcrane3576/. - Set up the
deployNamevariable by using therepovariable and thejobName(poc-micro) when creating thepipelineJob. - Set up the
testNamevariable by using therepovariable and thejobName(poc-micro) when creating themultibranchPipelineJob. - You can see the full contents of
seed.groovyin thepart2branch ofmicroservice-pipelineson github.
def buildPipelineJobs() {
def repo = "https://github.com/kcrane3576/"
def repoUrl = repo + jobName + ".git"
def deployName = jobName + "_deploy"
def testName = jobName + "_test"
createDeploymentJob(deployName, repoUrl)
createTestJob(testName, repoUrl)
}
buildPipelineJobs()
Goal 3
Since we will be setting up all of our stages in a Shared Library, we need to set up a groovy script (jenkinsJob.groovy) that the poc-micro service points to from its Jenkinsfile.
Adding jenkinsJob.groovy to microservice-pipelines
We are going to set up our jenkinsJob.groovy file to checkout our micro service code from source control and execute specific maven commands depending on the job that is running.
- Check out our microservice repository.
- Check out the workflow scm steps for more information.
- Read from the
environment variables(env.JOB_NAME) in order to obtain the Jenkins job name.deployName = poc-micro_deploy = env.JOB_NAMEtestName = poc-micro_test = env.JOB_NAME- Check out
Jenkins Set Environment Variablessection at theBuilding a software projectJenkins wiki for more information onenv.JOB_NAME.
Create and add the below code to vars/jenkinsJob.groovy in the part2 branch of microservice-pipelines.
def call(){
node {
stage('Checkout') {
checkout scm
}
// Execute different stages depending on the job
if(env.JOB_NAME.contains("deploy")){
packageArtifact()
} else if(env.JOB_NAME.contains("test")) {
buildAndTest()
}
}
}
def packageArtifact(){
stage("Package artifact") {
sh "mvn package"
}
}
def buildAndTest(){
stage("Backend tests"){
sh "mvn test"
}
}
Goal 4
In order for our micro services to execute in Jenkins, we need a Jenkinsfile in poc-micro.
Setting up our Jenkinsfile in our microservice
We will configure a Jenkinsfile in our microservices to point to our microservice-pipelines Shared Library.
- Note We are introducing the
version specifierfeature associated with the@Libraryannotation in Shared Libraries here. Within the@Libraryannotation, you will always need to provide the name of your Shared Library (e.g.@Library("microservice-pipelines)). However, if you add another@sign at the end of the Shared Library name (microservive-pipelines), you can tell yourJenkinsfileto read specific branches or tags from your Shared Library. In fact, in the code below, that is what we did. We are signaling ourJenkinsfileto use thepart2branch of our Shared Library with@part2(e.g.@Library("microservice-pipelines@part2")).
- At the root of your project, update the
Jenkinsfilewith the below code.
#!/usr/bin/env groovy
// Configure using microservice-pipelines and using "part2" branch
@Library("microservice-pipelines@part2") _
// Entry point into microservice-pipelines
jenkinsJob.call()
Running the seedJob
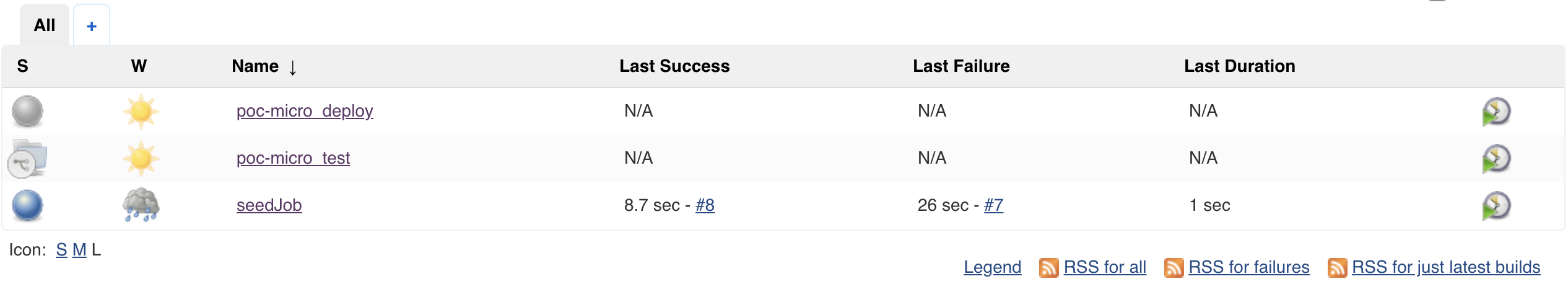
All of our configuration is set up and our repositories are ready to use. We will now run our seedJob to create our pipelineJob and multibranchPipelineJob based on our seed.groovy set up.
- Navigate to
Dashboard> selectseedJob-> selectBuild with Parameters> enterpoc-microinjobName> selectBuild.- Reminder Since we changed
seed.groovyon ourpart2branch ofmicroservice-pipelinesrepository, this script will require an admin approval in Jenkins.
- Reminder Since we changed
- Navigate to
Dashboard> selectManage Jenkins> selectIn-process Script Approval> selectApprove. - Navigate to
Dashboard> selectseedJob-> selectBuild with Parameters> enterpoc-microinjobName> selectBuild. - Navigate to
Dashboard> verifypoc-micro_testandpoc-micro_deployjobs were created.- You will need to repeat this step for all micro services you plan to onboard.
Running poc-micro_test job
Now you have a poc-micro_test job that will run every 5 minutes based on the cron we set up, but you can also trigger it manually.
- Navigate to
Dashboard> selectpoc-micro_test> selectmaster> selectBuild Now - Under
Build History, select the blinking blue circle (red if previous failure) > Observemvn testexecuting inConsole Output.
Running poc-micro_deploy job
We can also observe the poc-micro_deploy job executing mvn package.
- Navigate to
Dashboard> selectpoc-micro_deploy> selectBuild Now - Under
Build History, select the blinking blue circle (red if previous failure) > Observemvn packageexecuting inConsole Output.
Conclusion
During this series we set up a seed job that was used to create a pipelineJob (deploy job) and multibranchPipelineJob (test job) when onboarding our poc-micro micro service with our seedJob. Additionally, we set up our Shared Library to use jenkinsJob.groovy to handle the logic that determines which stages are executed depending on the currently running job (env.JOB_NAME). By using a combination of a "seed" job and Shared Libraries, you now have a foundation set up to onboard any number of services the same way while maintaining job specific stage execution. This provides you the ability to streamline your CI and CD requirements for microservices.


