In this day and age we are living in, it is not a luxury to have data streaming applications for interactive customer service and other aspects of business; it is becoming a necessity. Being able to react to requests as they happen has proven to be valuable and data streaming applications are what enable this new phenomena known as actionable intelligence. Apache NiFi is one of the tools that is at the core of this trend.
History
Before NiFi assumed its name at its birthplace, the NSA, it was known as Niagrafiles. It was a project aimed to address the issues of data flow in the context of security, interactivity, fault tolerance, scalability, routing, data transformation, conversion, encryption, governance, provenance, buffering with back-pressure, prioritized queuing, clustering, and many more. It was contributed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) in November 2014. When NiFi came out of the NSA, much of the original development team followed and started a company called Onyara to continue development and support for NiFi as an open source project. Hortonworks acquired Onyara and made it its Hortonworks Data Flow platform. Though it seems young to the open source industry, it has been used and tested in the NSA for several years before it was donated to ASF.
Architecture
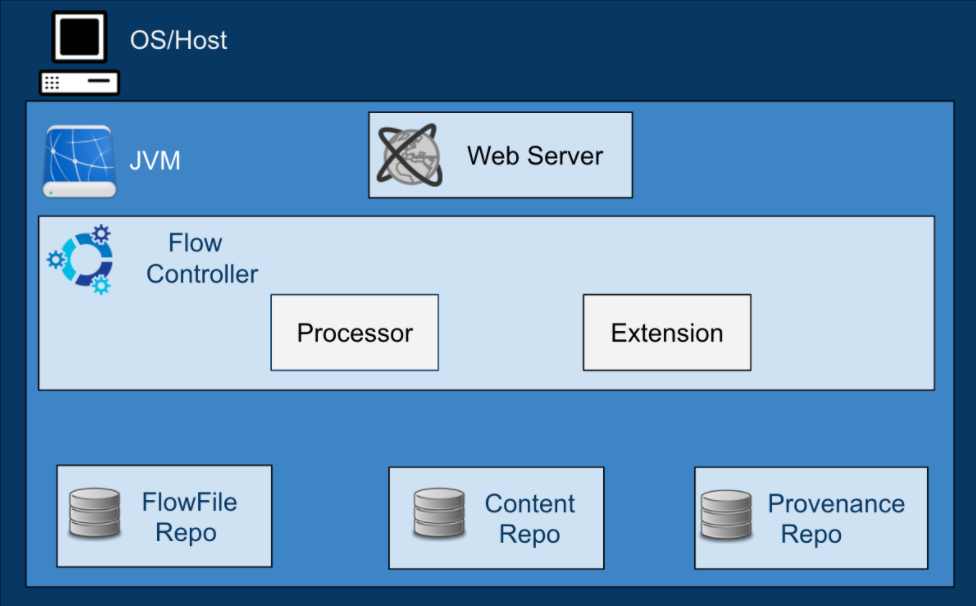
Web Server: Hosts NiFi’s HTTP-based command and control API to enable its flow-based programming.
Flow Controller: A broker that manages schedule and provides threads for extensions. It keeps track of connections and writes to Repositories.
Processor: Does the work. It is the building block of data flow in NiFi. It is an interface mechanism to expose access to FlowFiles, their attributes, and content.
FlowFiles: Core abstraction key/value pair metadata attributes that help manage the data flow. It is a pointer to the actual content that is written in the repository.
FlowFile Repo: A write-ahead-log, a method where a log is written before action is taken. It is used to enable durability and atomicity. It keeps key/value pairs of metadata flowing in the system.
Content Repo: This is where content is written.
Provenance Repo: An indexed audit style information that tracks each piece of data that moves through the system.
Use and Uniqueness
NiFi is a pull-based data ingestion system with per-event data transformation, filtering, and routing. It has the ability to be modified at runtime and extended via custom processors. When a certain processor is down, data is not lost, but queued and waiting for the inherent processor to be active. When it becomes active, the queue will unload to the processor, and the data flow will be in sync, guaranteeing at least one delivery.
It has very low latency and high throughput. Naturally asynchronous and built-in buffering makes NiFi efficient and resilient. It also has the capability to do concurrent tasks and run processes event-based, timer driven, or at a specific time. If latency is needed, it can be set to run every specified amount of time instead of streaming data real time by using the Run Schedule on a Processor.
NiFi has a language used to configure Processor properties. It enables developers to dynamically update, delete and modify files, alter FlowFile attributes, perform mathematical operations, perform string and date manipulations, and many more.
NiFi has the ability to encrypt data in motion. The processor “EncryptContent” is used to encrypt data with six key derivation functions and 25 encryption algorithms, with the default being Bcrypt and MDS_128AES respectively.
NiFi’s zero-master clustering has enabled data agility, scalability, and eliminated single point of failure. Leveraging Apache ZooKeeper as coordinator, NiFi is able to cluster multiple nodes with one node behaving as a cluster coordinator and another as a primary node to avoid redundant unnecessary tasks and having resources compete for the same data. Each node on a clustered NiFi operates on given data, sharing it, but works on a distinct set of the data.
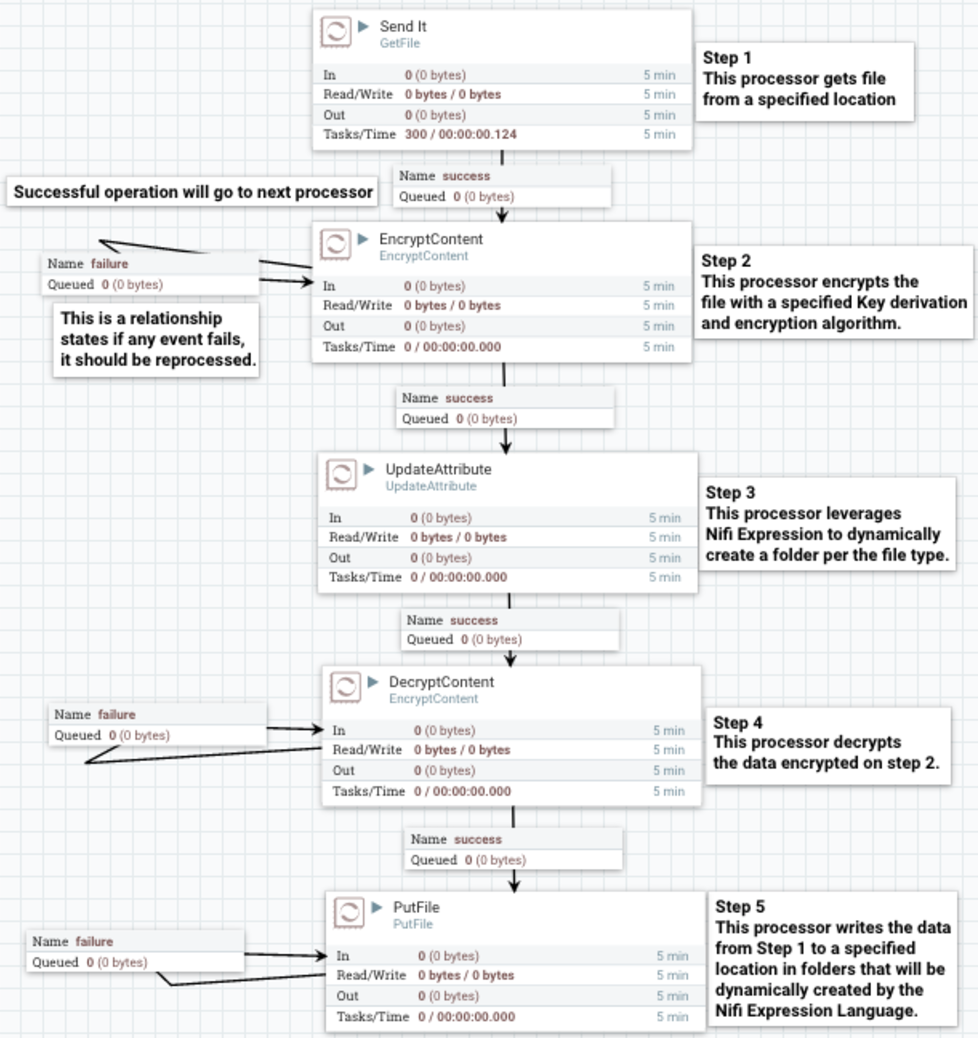
Here is an example of a NiFi DataFlow:
NiFi Administration Tools
NiFi has easy to use administration tools:
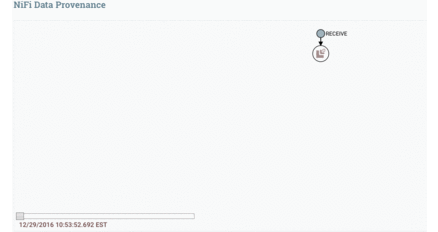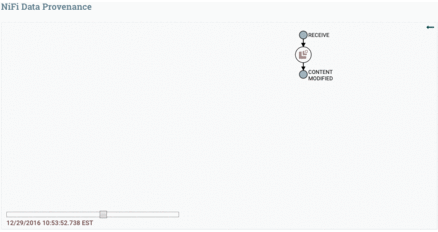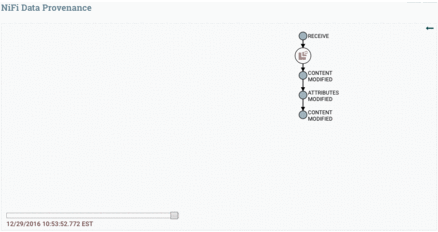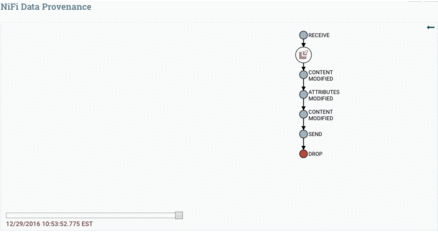
Data Provenance is used for tracking data in motion, enabling users to see how data in motion was processed and what processor processed it at a specific time.
Here is the Data Provenance GIF for the above example:
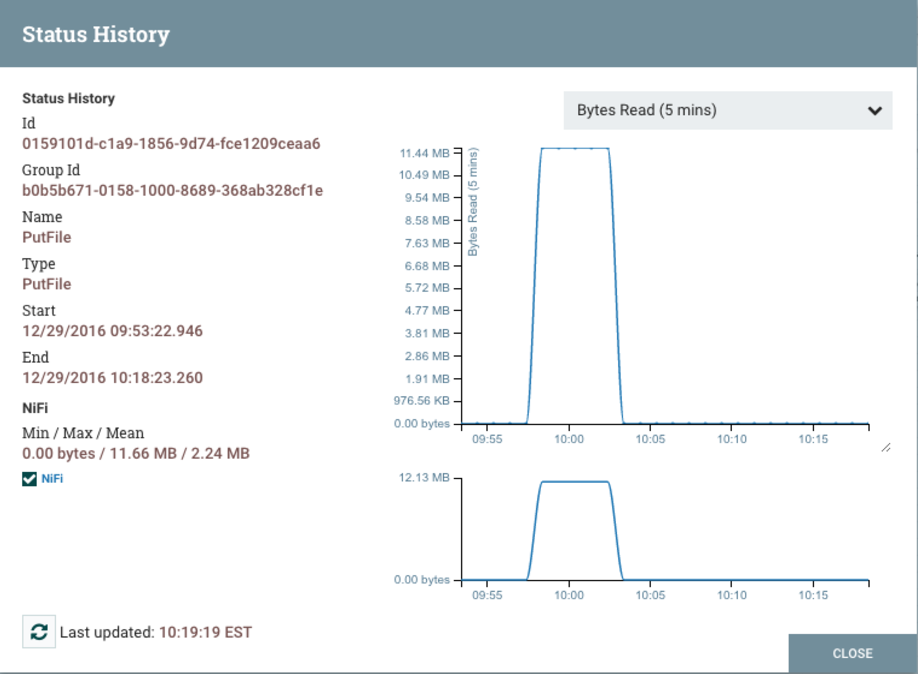
Status History is a tool that shows the amount of data a processor has processed in a given timeframe.
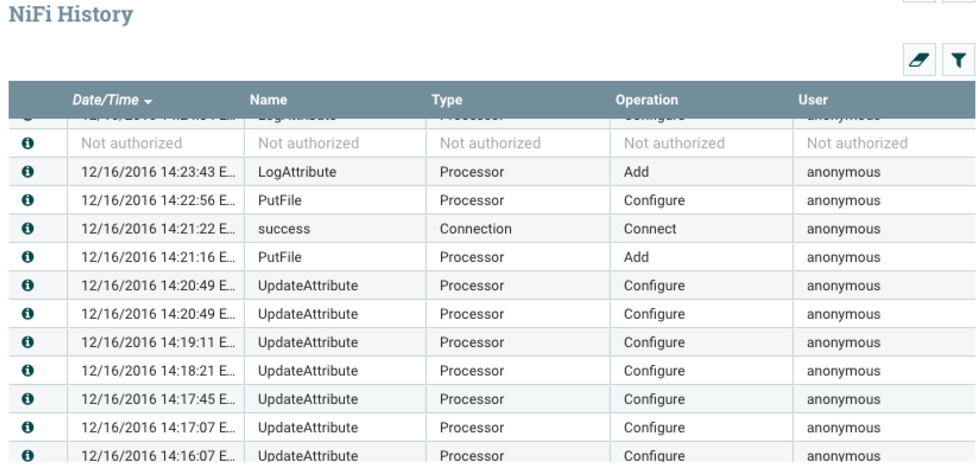
For auditing purposes, Configuration History is used to track when and who updated any connection, configuration, or processor.
Conclusion
Known as the Swiss Army Knife of data flow, NiFi is a framework for managing complex data flows. Its flow-based programming makes it easy to use and learn. It is a cross platform application with easy installation, configuration, and runtime. It is highly scalable, agile, flexible, durable, and resilient.
One drawback is its lack of performance in transferring large batches of data, as benchmarking is needed.
In the next article, we will take a look at Apache Hive and how NiFi integrates with it.



